PRINCIPLE OF WIDAL TEST
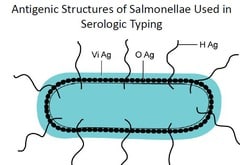 Patients infected with Salmonella produce antibodies against the antigens of the organism. Antibodies in serum, produced in response to exposure to Salmonella organisms will agglutinate bacterial suspension which carries homologous antigens. This forms the basis of Widal test.
Patients infected with Salmonella produce antibodies against the antigens of the organism. Antibodies in serum, produced in response to exposure to Salmonella organisms will agglutinate bacterial suspension which carries homologous antigens. This forms the basis of Widal test.The organisms causing enteric fever possesses two major antigens namely somatic antigen (O) and a flagellar antigen (H) along with another surface antigen, Vi. During infection with typhoid or paratyphoid bacilli, antibodies against flagellar antigen of S. typhi (H), S. paratyphi A (AH), S. paratyphi B (BH) and Somatic Antigen of S.typhi (O) usually become detectable in blood, 6 days after the onset of infection.
Those antigens specifically prepared from organism are mixed with patient’s serum to detect the presence of antibodies. Positive result is indicated by the presence of agglutination Absence of agglutination indicates a negative result. The paratyphoid O antigens are not employed as they cross react with the typhoid O antigen. If agglutination occurs with O antigen then it is considered positive for Salmonella typhi. If agglutination occurs in A or B antigen then it is confirmed as positive for Salmonella paratyphi. Agglutination will occur in H antigen for all the cases of antigens like O, A, and B.
PREPARATION OF ANTIGENS
Antigen suspensions may be prepared from suitable stock cultures in the laboratory. But generally commercially prepared suspensions are used.
- Salmonella typhi is used to prepare S. typhi O and S. typhi H antigens.
- O antigens for S. paratyphi A and S. paratyphi B are not taken as they cross-react with S.typhi O antigen.
- H antigen suspension is prepared by treating overnight broth culture or saline suspension of Salmonella with 0.1% formalin.
- For preparing O antigen suspension, Salmonella are grown on phenol agar (1:800) to inhibit flagella. The growth is then emulsified in small volume of saline, mixed with 20 times its volume of alcohol, heated at 40°C to 50°C for 30 minutes and centrifuged.
- The antigens are treated with chloroform (preservative) and appropriate dyes are added for easy identification of antigens.
PROCEDURE OF WIDAL TEST
The Widal test can be conducted in two ways :
- Slide agglutination Widal test
1. Qualitative Slide Test
2. Quantitative Slide Test - Tube agglutination Widal test
Tube agglutination has more accuracy as compared to the slide agglutination technique. However, A slide widal test is more popular among diagnostic laboratories as it gives rapid results.
Qualitative Slide Test
Procedure :
- Bring all reagents to room temperature and mix well.
- Add 1 drop of test sample (25µl) into each reaction circle labeled as O, H, AH, BH according to given antigen solution.
- Add 1 drop of positive control (25µl) into the circle marked as PC and 1 drop of negative control (25µl) into the reaction circle marked as NC.
- Add antigen solutions of Salmonella typhi ‘O’, Salmonella typhi ‘H’, Salmonella paratyphi ‘AH’ and Salmonella paratyphi ‘BH’ to circles labeled as O, H, AH, BH respectively in which test samples has been added.
- Mix it thoroughly with the aid of applicator stick and rotate the slide gently.
- Observe for agglutination.
Interpretation :
- Positive Test : Agglutination within a minute
- Negative Test : No agglutination
Quantitative Slide Test
This is performed for the samples which showed positive agglutination during qualitative test.
Procedure :
- Bring all reagents to room temperature and mix well.
- Dispense one drop of saline into the first reaction circle and then place 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 ul of the test sample on the remaining circles.
- Add a drop of the antigen, which showed agglutination with the test sample in the screening (qualitative) method, to each circle.
- Mix the contents of each circle with the aid of applicator stick and rotate the slide gently.
- Observe for agglutination.
Interpretation :
The antibody titre of the test sample is its highest dilution that gives a visible agglutination. 80 µl corresponds to 1 in 20 dilution, 40 µl to 1 in 40, 20 µl to 1 in 80, 10 µl to 1 in 160 and 5 µl corresponds to 1 in 320 titre. Agglutinin titre greater than 1:80 is considered as significant infection and low titres indicate absence of infection.
Quantitaive Tube Test
Procedure :
- Bring all reagents to room temperature and mix well.
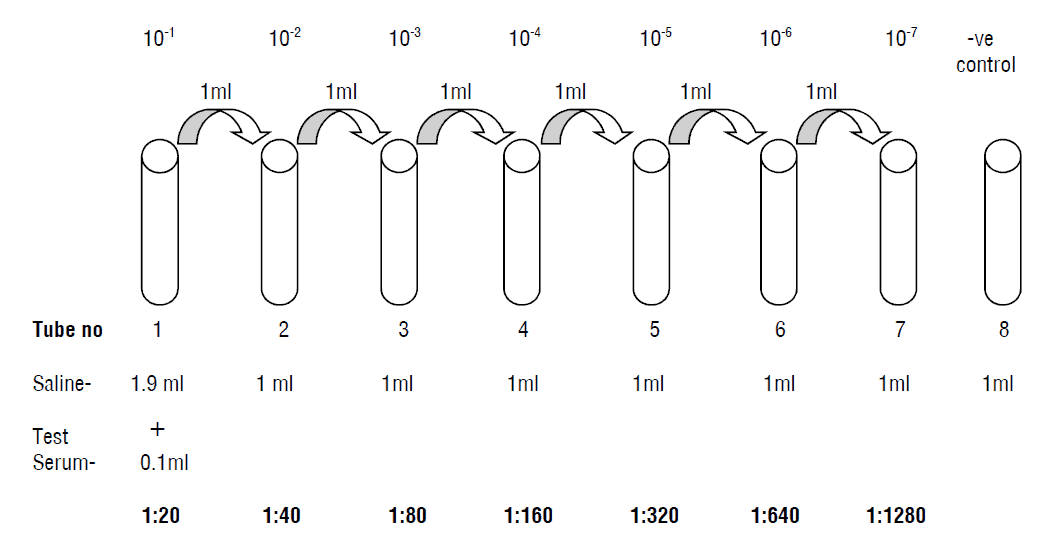
- Prepare 4 sets of test tubes for individual antigen. Each set contains 1- 8 tubes.
- Add 1.9 ml of 0.85% sterile saline to tube no. 1 of each antigen set.
- To tube no. 2-8 of all sets add 1 ml of physiological saline.
- To tube No. 1 of all sets add 0.1 ml of test sample to be tested and mix well.
- Transfer 1 ml of the diluted serum sample from tube No. 1 to tube No. 2 and mix well.
- Transfer 1 ml of the diluted serum sample from tube No. 2 to tube No. 3 and mix well. Continue this serial dilution till tube No. 7 in each set of antigen.
- Discard 1.0 ml of the diluted serum from tube No.7 of each set.
- So the dilutions of the serum sample from tube No. 1 to 7 respectively in each antigen set are 1:20, 1:40,1:80, 1:160, 1: 320, 1:640, 1: 1280.
- Tube no. 8 is negative control with 0.85% sterile saline.
- To one set i.e. from tube no.1- 8 add 50 µl of Salmonella typhi ‘O’ antigen.
- In second set i.e. from tube no.1- 8 add 50 µl of Salmonella typhi ‘H’ antigen.
- Respectively for third and fourth sets, add Salmonella paratyphi ‘AH’ and Salmonella paratyphi ‘BH’ to all tubes from 1-8.
- Mix well, cover and incubate these tubes overnight at 37 degree Celcius (approximately 18 hours).
- After incubation dislodge the sediment and observe for agglutination.
Interpretaton :
The antibody titre of the test sample is its highest dilution that gives a visible agglutination. Agglutinin titre greater than 1:80 is considered as significant infection and low titres indicate absence of infection.
LIMITATIONS OF WIDAL TEST
- Tests done within 7 days of illness and after 4 weeks are usually negative.
- The local titre of the place should be known for the results interpreted correctly.
- This test (Quantitative) is highly time consumable.
- Previous typhoid vaccination may contribute to elevated agglutinins in the non-infected population.
- Other infections of non-enteric salmonella infection such as Typhus, Immunological disorders, chronic liver disease may cause false positive reaction.
- Cross reaction between malaria parasites and salmonella antigens may cause false positive Widal agglutination test

No comments:
Post a Comment